
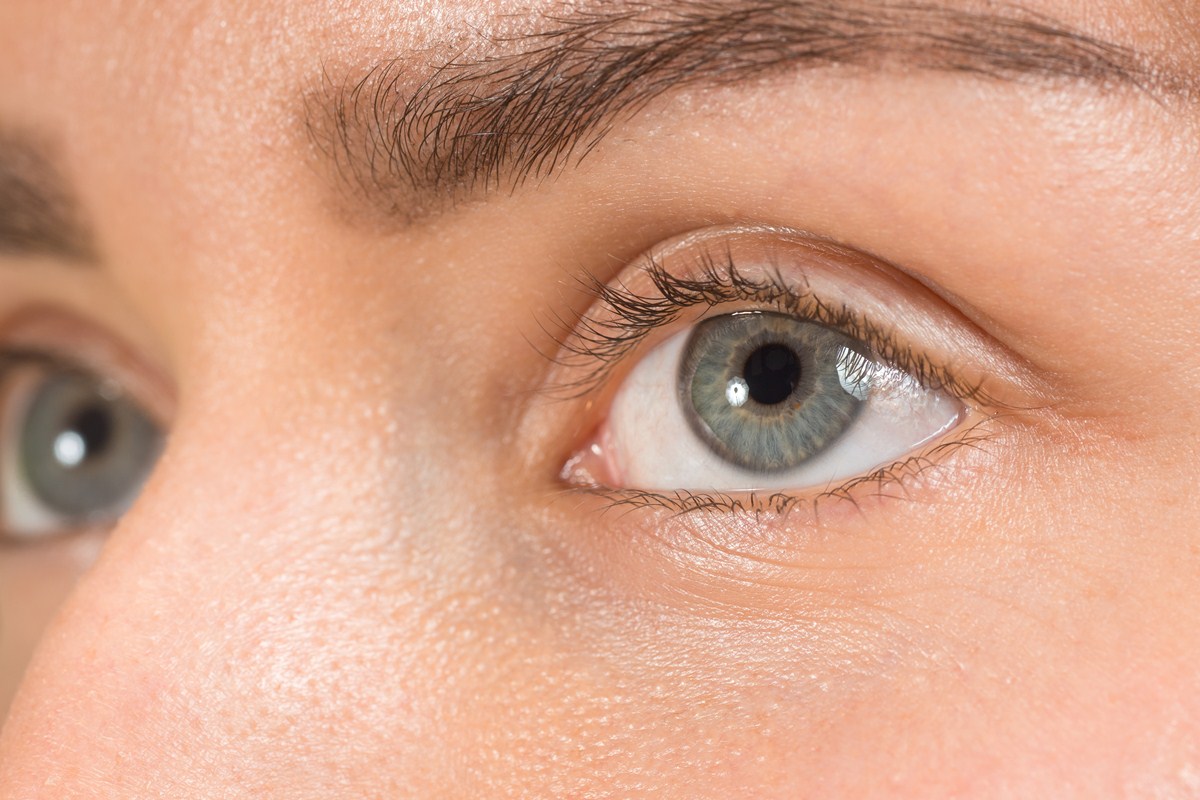
The eye may lose its normal cat’s eye red reflex due to cataract, retinal detachment, or blood or other abnormalities within the eyeĪ white pupil is seen in advanced cataract and a range of serious conditions of the vitreous or retinaĪbnormalities of the pupils often indicate potentially serious underlying problems and should be assessed by an ophthalmologist. Urgent referral is indicated for abnormalities in children, those of sudden onset or progressing, and those with associated pain or loss of vision. Subsequently, there is a loss of visual clarity. As a consequence, light cannot travel through to the retina. Cataracts: A cataract develops when the lens of the eye becomes cloudy or ‘opaque’. Misshapen pupils are seen due to adhesions to the lens following intra-ocular inflammation (synechiae), trauma, congenital abnormalities such as coloboma or aniridia, or iris tumours. In cats, this often occurs due to a lack of the amino acid Taurine. However, in more severe cases vision is permanently lost and sometimes other neurological problems are also present. Common signs and symptoms include: A persistently small pupil (miosis) A notable difference in pupil size between the two eyes (anisocoria) Little or delayed opening (dilation) of the affected pupil in dim light.

The pupils may not be identical in size due to natural physiological variation.Ībnormally large pupils are seen in Holmes-Adie syndrome (one eye, fails to contract to light), with third cranial nerve palsy (usually with associated double vision and/or ptosis, fails to contract to light), eye-drops, or drugs such as cocaine.Ībnormally small pupils are seen with Horner’s syndrome (one eye, often with slight ptosis), eye-drops (eg pilocarpine for glaucoma), drugs such as morphine or, rarely, stroke. Post-traumatic sarcoma within the eye occurs in older cats with a history of longterm inflammation of the uvea (chronic uveitis Inflammation of the Anterior Uvea The uvea (or the uveal tract) is the colored inside lining of the eye consisting of the iris, the ciliary body, and the choroid.The iris is the colored ring around the black pupil. Horner syndrome usually affects only one side of the face. In the mirror, the pupil of the eye appears as a black circle in the middle of the iris (the colored part of the eye). Pupils may be abnormal in terms of size, shape or reactions or the normal cat’s eye red reflex may be lost. Pupillary Disorders Including Anisocoria.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
